
One of the research facilities dedicated to advancing the world of nuclear fusion has succeeded in showing us once again that, despite the fact that many experts still call for calm because there is still a long way to go to that the human being can use nuclear fusion as a source of energy, the truth is that we are much closer than we can imagine.
The team that has managed to make the news, despite the fact that it is usually recurrent in this field, has been the one that works in the field of nuclear fusion since Germany. Specifically, we are talking about an installation, the same one that we have already talked about on occasion, and that at the time was equipped with a Stellarator Wendelstein 7-X, a device specially designed so that, thanks to the use of magnets, it can confine plasma clouds inside.
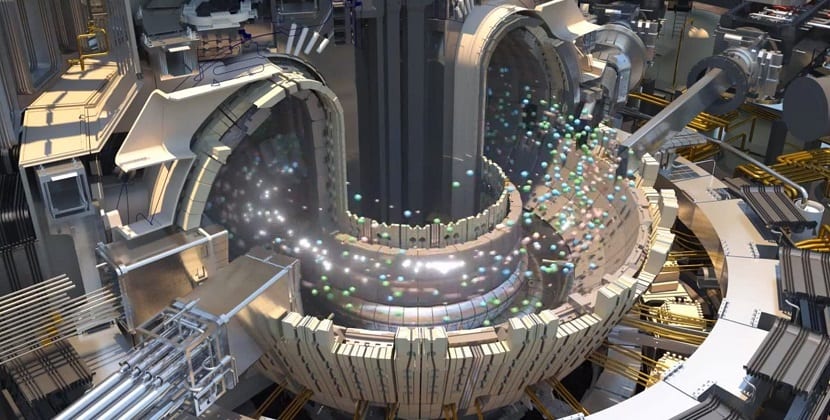

German stellarator achieves new milestone in nuclear fusion race
At this point and before continuing, I always like to remember that in this post we are not talking about all those power plants scattered throughout our country, which do not use nuclear fusion techniques as such, but rather use nuclear fission to create energy. The different between fusion and fission is that while in fusion two atoms are sought to unite creating one, in fission it is the opposite, that is, an atom is decomposed into two.
In favor of nuclear fusion, for example, we have that it does not produce radiation. To this, in turn, we must add the enormous amount of energy that we can generate. The supply can be so extensive that there have been many authorized voices within this complex field who do not hesitate to denominate this source of energy as unlimited, at least theoretically.
Many have been the resources, both human and financial, invested in this project
Going back to the experiments that are being carried out in Germany, remind you that the Wendelstein 7-X was turned on for the first time at the end of 2015 showing that, for a tenth of a second, it could hold in place a cycle of helium ions heated to a million degrees. Perhaps this sum of time may not seem like too much if we want to supply ourselves with energy thanks to the use of a platform like this, although, in favor of the engineers and physicists who operate it, it should be noted that it has not been built to create energy, but rather it is not nothing but a test bed where we can find a way to squeeze as much of nuclear fusion technology as possible.
During the last tests carried out, it has been working with an energy 18 times higher than the previous tests. Specifically, we are talking about helium ions compressed through a plasma at a temperature of 40 million degrees Kelvin. Although the temperature is up to 4 times higher than in previous tests, the truth is that for to get two atoms to fuse it is estimated that we must reach 100 million degrees.
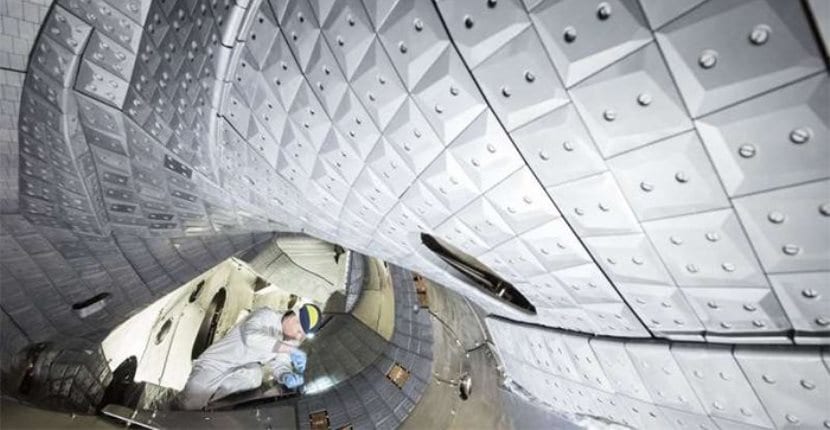

There is still a long way to go until humans master nuclear fusion
On the other hand, it should be noted that not only has it been possible to work with much higher temperatures, but also that the team of engineers and physicists working on this project has achieved increase the condensation time to 6 seconds. We are not talking about hours yet, but the progress is much more significant than we can imagine due to the size of the data.
To achieve these improvements, the stellarator had to be equipped with a new type of inner lining that helps to control the flow of the plasma by diverting the dispersed particles that affect the plasma itself. As expected and this has been confirmed, especially as a result of the statements of those responsible for the project, from now on work will be done on testing changes in this coating in order to achieve higher plasma densities with higher temperatures.