
If you are a lover of quantum computing, surely the title of this same post has been more than surprising, if on the contrary you are not very up to date with what is happening in this world, surely the title, the less it has left you enough ice cream, not knowing exactly whether to celebrate something or not. To get out of any doubt, tell you that we are facing nothing less than an unprecedented milestone.
Specifically, we are facing a new record in terms of quantum computing, same that contrary to what you can imagine, this time, it has not been harvested by companies of the size and investment in this area such as IBM, Google or Microsoft, but it corresponds to a team of scientists from the Rainer Blatt experimental physics laboratory of the University of Innsbruck (Austria).
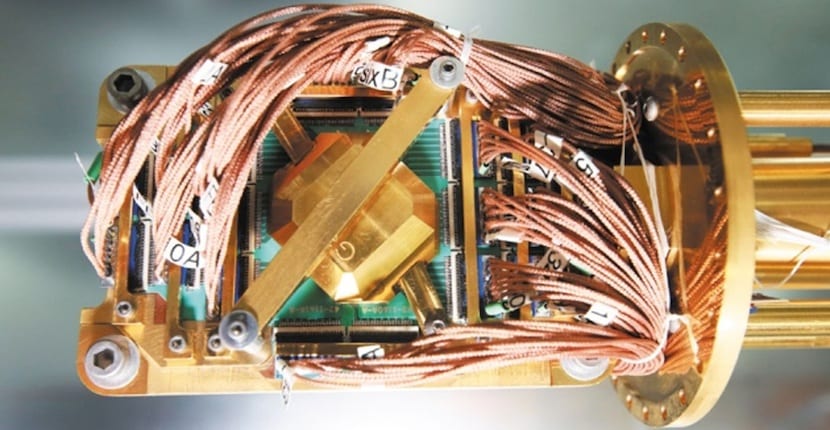
Many are the institutions that seek to create the best quantum computer although, for the moment, this record is held by the University of Innsbruck
Far from this race to be the owners of the most powerful and capable quantum computer on the planet, something that seems sooner or later Google will achieve with its new 72-qubit quantum processor, falls precisely on the University of Innsbruck, at less, as has been the case, in Google they can measure each qubit of their system and can put the name of their institution next to a new record.
To try to understand a little better why quantum computing is so relevant at the moment, we could say, as can be read elsewhere, that a qubit is similar to a traditional bit and, this is where all the similarities end, since a Traditional bit, as we know it, has two different states that are usually represented as 0 and 1. As for qubits, we are talking about pairs of entangled atoms that can have either of these two states simultaneously.
Thanks precisely to the fact that a qubit can have superimposed states, the theoretical power that a quantum processor can reach is multiplied. Basically and on paper, a quantum computer could perform complex operations in a matter of seconds, the same as a traditional computer would take decades. Unfortunately, due to this superposition of states, we must know the specific state without the possibility of error to create a stable register, otherwise, we would only have a processor full of atoms that would not contribute anything.
In order to stabilize up to 20 qubits, calcium ions have been used subject by magnetic fields
One of the great peculiarities presented by the project carried out by the team of researchers from the University of Innsbruck is to know that, in order to stabilize the qubits of its platform have used calcium ions held by an ion trap where magnetic fields are used. To this we must add that, in order to interlace the qubits, different laser systems have been used.
For this test, a new detection method has been created for the state of each qubit individually. This new method has required the development of a new methodology that requires a greater calculation but, as an advantage, it should be noted that it is much more effective and accurate. To get an idea of its effectiveness, note that those responsible for this project have achieved verify the formation of triplets and groups of up to four and five interlocking qubits.
As those responsible for the project have commented, the next step is to interlace a maximum of up to 50 qubits with independent measurement of each one of them. As a detail, tell you that, in case they achieve this goal, We will be facing that leap necessary for any quantum computer to be more powerful today than any of the current supercomputers.
Further information: science alert