We have all heard the words quantum computer at some time, but generally very few know what it really is. For many, the first thing that comes to mind is a very powerful personal computer, capable of performing any task but at maximum speed, but it is not a simple super powerful computer, It's much more than that.
Although these are machines totally out of reach of the general public, they generate a lot of curiosity. In this article we explain what a quantum computer is and what it is generally used for and what are the quantum phenomena on which its power is based.
What is a quantum computer?
Quantum computers are mammoth machines that take advantage of some phenomena of quantum mechanics to achieve large increases in processing power. Quantum computers are capable of keeping up with the bitumen to any traditional super desktop computer. Something that is often referred to as quantum supremacy.
Does this mean that we will all end up having a quantum computer at home to surf the internet or play video games? Absolutely not. Classic machines will continue to be the usual solution both to solve our problems and on which to base our interactive leisure. Also the most economical.
Quantum computers promise to be a boost for various fields of technological advance, such as science, medicine or genetics. Some companies are already starting to use them to develop their new products, such as new lighter and more durable materials to completely replace thermal fuel.

How does a quantum computer work?
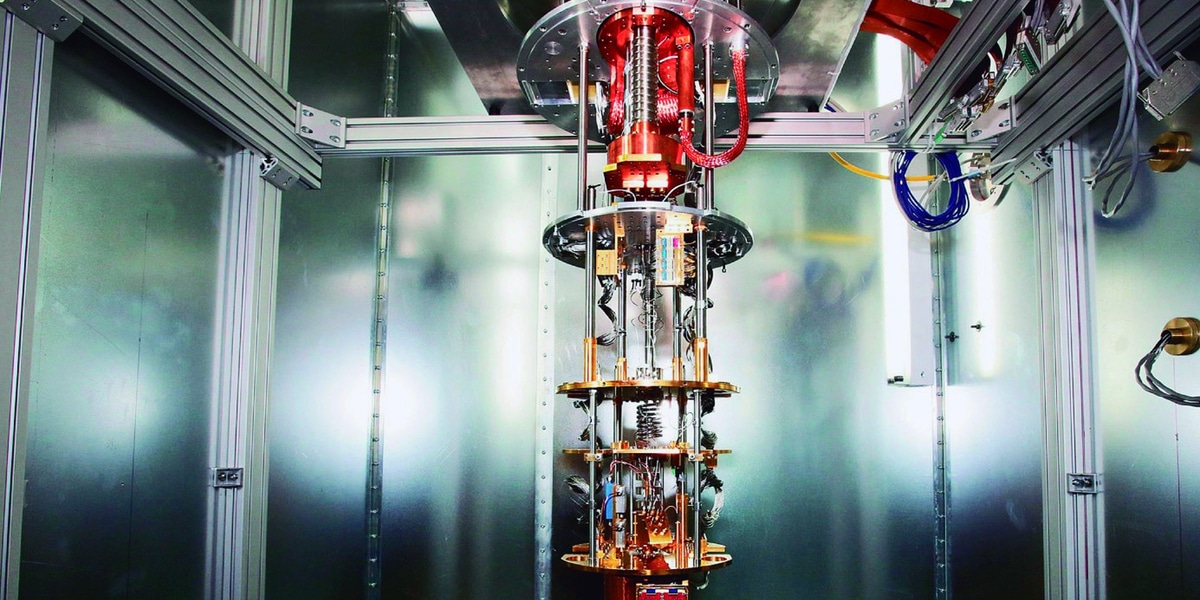
These machines they do not base their power on conventional hardware, like the one we can find in our home computers, it is not about large-scale graphics cards and processors, it goes much more than that, both in quantity and complexity. The secret of the power of a quantum computer lies in its ability to generate and manipulate quantum bits or qubits.
What is a Qubit?
Traditional computers use bits, megabytes, gigabits…. A stream of electrical or optical pulses representing ones and zeros. The entire virtual world from an email, a website or a movie that we see online, are essential to a long chain of zeros and ones.
Quantum computers use qubits, subatomic particles like electrons or photons. The approach of some companies like Google relies on superconducting circuits cooled to temperatures lower than deep space. Others trap individual atoms in electromagnetic fields on a silicon chip, in a vacuum chamber. In both cases the goal is to isolate the qubits to a controlled quantum state.
Qubits have some peculiar properties, which make a group of them capable of giving much more processing power than the same number of binary bits. The most important are called superposition and quantum entanglement.
What is quantum superposition?
Quantum superposition occurs in nature, when an elementary particle simultaneously possesses two or more states, as happens with photons, which they can stay in two different places at the same time, something unimaginable in the ordinary physical world.
This property is also observed in other particles such as electrons or neutrons, in atoms or even in small molecules. This journey has led scientists to wonder where the boundary is between the quantum world and what we call the real world, when a particle ceases to be quantum and is subjected to known physical laws.
Thanks to this phenomenon, a quantum computer with several overlapping qubits can arrive at a large number of possible results simultaneously.
Quantum entanglement
You can generate pairs of "entangled" qubits, whereby both exist in the same quantum state. Change the state of one of the qubits it would instantly alter the other's state in a predictable way, this happens even if you are far apart.
It is not known for sure how or why quantum entanglement actually works. Something that was able to confuse Albert Einstein himself, who would describe it as "a terrifying action at a distance". Entanglement is vital for quantum computers to acquire their great power. In a conventional computer, doubling the number of bits doubles its processing power. In the case of a quantum computer, adding additional qubits produces an exponential increase in its capacity.
These machines take advantage of the qubits entangled in a kind of quantum daisy chain to perform operations. The ability of machines to speed up calculations with specially designed quantum algorithms is the reason they generate so much excitement.
However not everything is exceptional when it comes to quantum computers, since they are very susceptible to errors, due to computational inconsistency.
Inconsistency
This is a phenomenon that causes quantum behavior to decay and finally disappear due to the interaction of qubits with their environment, since their quantum state is very fragile. A slight vibration or a change in temperature can cause these to come out of the overlap before the task is complete. For this reason, qubits are usually stored in refrigerators and vacuum chambers at a very low temperature.
Google's quantum computer
Google has not wanted to be left behind when it comes to quantum technology, the North American giant has developed a quantum computer capable of performing a calculation in 200 seconds, which in a traditional super pc would have taken ten thousand years. That is why it proclaims that quantum computers are the immediate future. Although its competition IBM does not end up agreeing.
Neutral researchers show that Google's quantum computer had to perform a random number calculation that could only be successful if all the computer's components were working in perfect harmony.
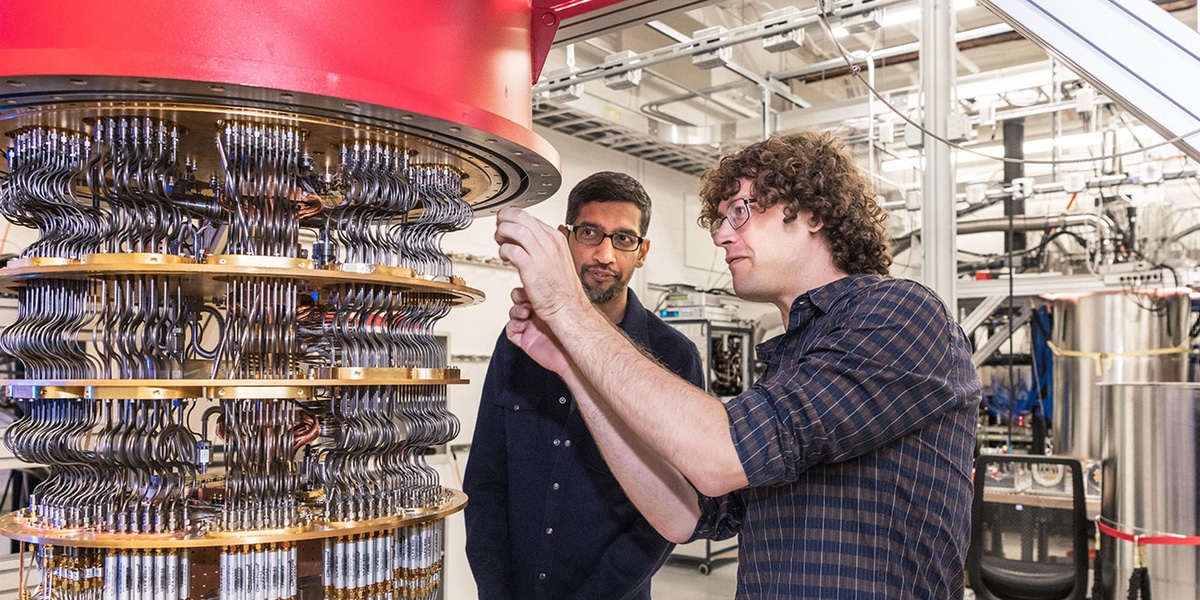

Google does not plan to fall behind in this race and therefore promises to invest much more capital in this technology. In the case of Google, we can guess that this will be the case, although IMB does not intend to sit idly by since most of its resources are currently being devoted to improving this technology. Time will tell if Google is capable of developing quantum supremacy on its own or will it need to join its competition.
It is a technology that can benefit us all, in the development of medicines capable of curing diseases incurable so far.